Analysis of the Impact of the Margin Requirement Ratio Hike on A-Share Market Liquidity and Leverage Levels
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features

About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
Related Stocks
Based on the obtained market data and research reports, I will conduct a systematic in-depth analysis for you.
On January 14, 2025, the three exchanges in Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Beijing simultaneously issued a notice to raise the margin requirement ratio for margin trading from 80% to 100%, and the policy will be officially implemented on January 19, 2025[1][2].
| Indicator | Previous Rule (80%) | New Rule (100%) | Change Magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Leverage Ratio | 1.25x | 1x | 20% Reduction |
| Financed Amount with RMB 1 Million Margin | RMB 1.25 Million | RMB 1 Million | RMB 250,000 Reduction |
| Total Position with RMB 1 Million Margin | RMB 2.25 Million | RMB 2 Million | 11.1% Reduction |
As of January 12, 2025, the balance of margin trading and securities lending in the A-share market reached approximately
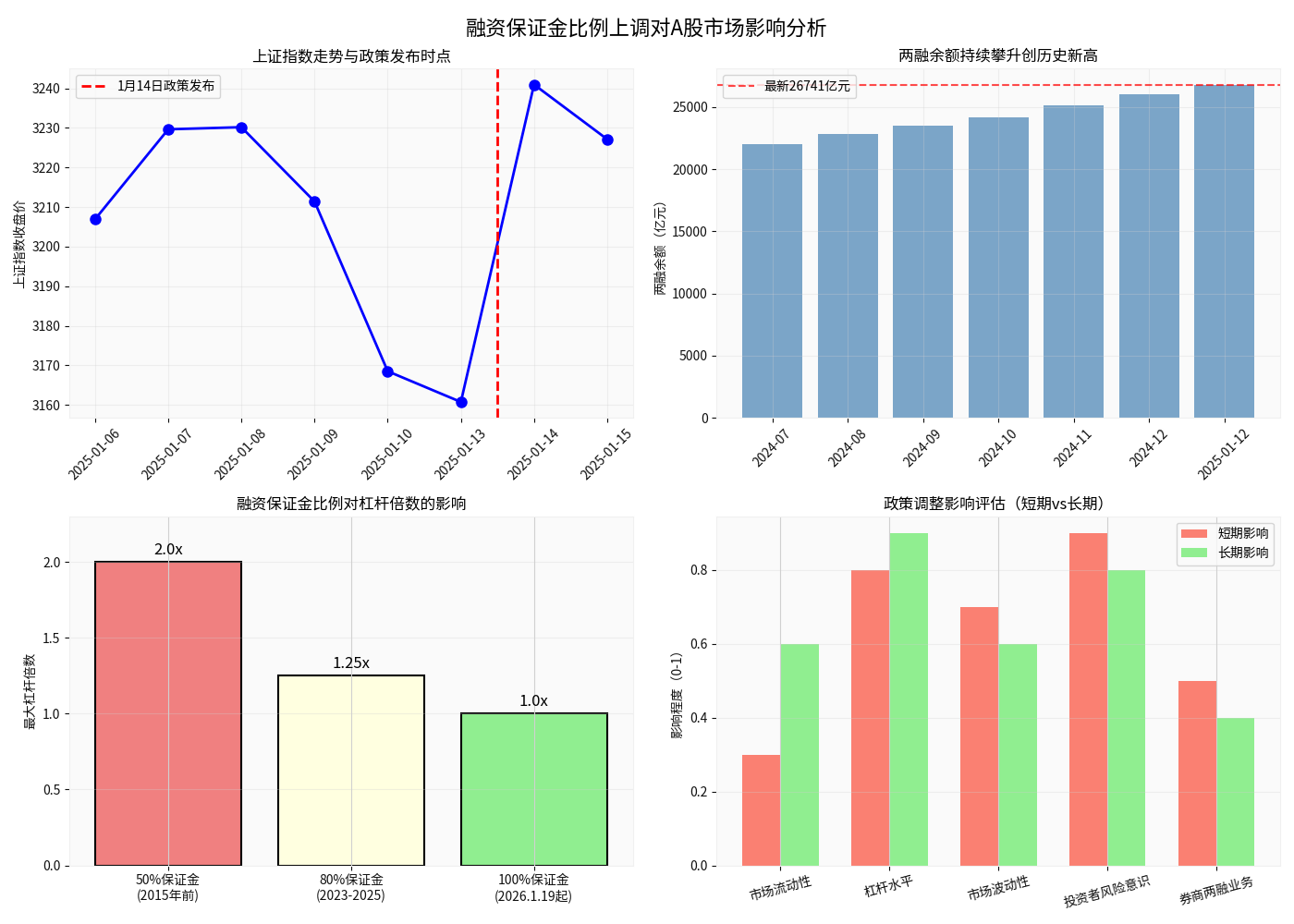
- The market will go through a sentiment release period, and high-leverage sectors may see a 10%-20% correction[1]
- Trading volume may remain at a high level, but market divergences will widen, leading to fierce long-short games
- Some sectors and stocks that rely on margin trading speculation will face short-term funding pressure
- The ratio of margin trading balance to A-share free float market capitalization is only 2.58%, far lower than the historical peak of4.72%[2]
- The market’s maintenance margin ratio is as high as 288.77%, with overall risks under control[2]
- The proportion of leverage-funded capital will decline, and long-term capital and value investment will become the mainstream
Since 2025, margin trading business at securities firms of all sizes has shown significant growth, with the overall industry growth rate ranging from
| Type of Securities Firm | Business Performance | Representative Institutions |
|---|---|---|
| Leading Brokers | Outstanding capital strength and client resources | Huatai Securities, China Merchants Securities, Orient Securities |
| Regional Mid-Sized Brokers | Rapid growth, with some seeing 30%-40% growth | Changjiang Securities, Zheshang Securities |
| Individual Brokers | Margin trading funds exhausted, implementing quota restrictions | Hualin Securities, Sinolink Securities |
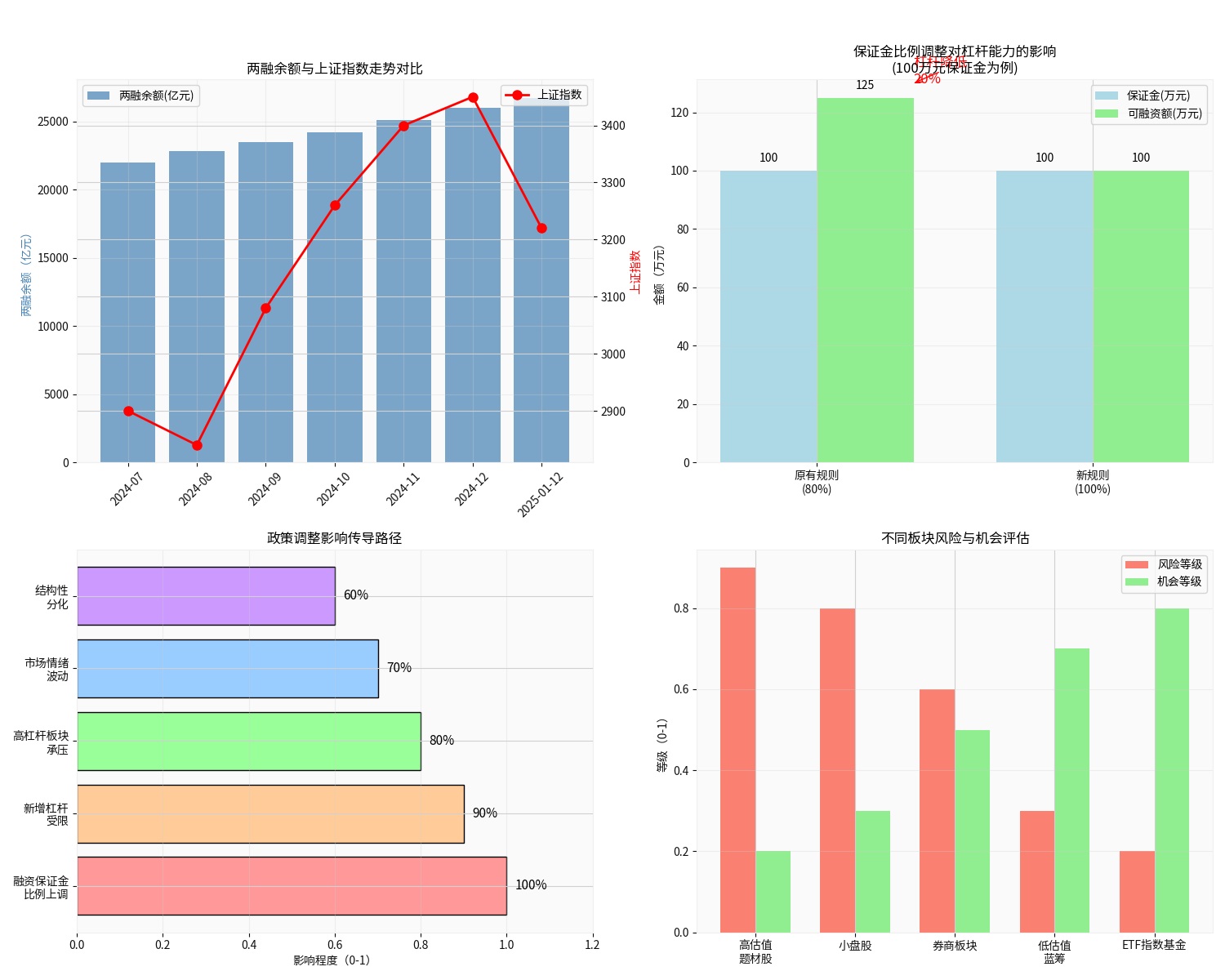
- New leverage capacity is directly reduced by 20%[1]
- The overall market leverage ratio will drop from 1.25x to 1x
- Effectively prevents market overheating risks and creates conditions for long-term healthy development
It is worth noting that although the margin trading and securities lending balance continues to rise, the ratio of margin trading turnover to A-share total turnover
- Although the current market leverage ratio is high, it has not reached the historical extreme level
- The policy adjustment is more of a counter-cyclical regulationmeasure rather than a crisis response
- It helps guide the market towards a ‘long-term, slow bull’ pattern
- The ratio of margin purchase volume to total turnover reached 10.3%in December 2025, higher than the annual average of9.8%[1]
- Some high-leverage, high-valuation sectors face correction pressure
- Local liquidity risks of “longs liquidating longs” may emerge
| Sector Type | Risk Level | Cause Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| High-Valuation Theme Stocks | High | Concentrated leverage capital, high valuation correction pressure |
| Small-Cap Stocks | Relatively High | Relatively weak liquidity, high volatility |
| Brokerage Sector | Medium | Margin trading business restricted, but supported by performance |
| Low-Valuation Blue Chips | Relatively Low | Shift in capital preference, good defensiveness |
| ETF Index Funds | Low | Risk diversification, institutional allocation demand |
- Effectively reduces the market leverage ratio and mitigates the cascading decline effect caused by margin calls[2]
- Enhances the risk resistance of the A-share market and promotes the return of the valuation system to value investment
- Aligns with international mature markets (most markets have a 100% margin requirement ratio)
- If leverage capital remains active in the future, further regulation cannot be ruled out[1]
- Measures may include adjusting the scope of margin trading targets and raising the margin requirement ratio for securities lending
- Uncertainty in policy expectations may increase market volatility
- Reduce Leverage Positions:The leverage ratio for newly opened margin trading contracts has decreased, requiring a re-evaluation of leverage strategies
- Avoid High-Leverage Targets:Reduce allocation to stocks with high margin trading ratios and small-cap theme stocks
- Monitor Maintenance Margin Ratio:Closely monitor account risks to ensure sufficient safety margins
- Margin trading capital shows new characteristics in ETF allocation: fixed-income products and CSI Short-Term Bond ETFs are favored[1]
- Broad-based index ETFs (CSI 300, CSI 500) continue to receive net margin purchases
- Low-valuation, high-dividend value stocks will gain capital favor
- Low-valuation blue chips: strong defensiveness, good liquidity
- Broad-based index ETFs: risk diversification, suitable for regular fixed-amount investments
- Growth stocks with high performance certainty: focus on industrial upgrading directions
-
Limited Liquidity Impact but Structural Divergence:The policy adjustment has a limited impact on existing funds, but the scale of new funds entering the market will be restricted, leading to structural divergence in the market.
-
Leverage Level Effectively Reduced:The margin requirement ratio hike directly cuts new leverage by 20%, helping to prevent market overheating risks.
-
Upward Potential Constrained but Trend Unchanged:Tight margin trading quotas at securities firms and policy tightening will restrict short-term market performance, but historical data shows that margin requirement ratio adjustments are not the decisive factor determining the broader market direction[2].
-
Long-Term Beneficial to Market Development:By reasonably managing market leverage ratio, the risk resistance of the A-share market is enhanced, promoting the market’s evolution towards a mature market.
[1] Eastmoney - In-Depth Research Report on the Impact of Margin Requirement Ratio Hike on A-Share Market (https://caifuhao.eastmoney.com/news/20260114143738860193110)
[2] CLS - After Two Years, Margin Requirement Ratio Returns to 100%: How Did A-Shares Perform After Previous Adjustments? (https://www.cls.cn/detail/2257341)
[3] CLS - New Margin Trading Accounts Hit a 10-Year High of 1.54 Million! Total Accounts Nearly Double Compared to 2016 (https://m.cls.cn/detail/2254540)
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
