Analysis of the Impact of South Korean Won Exchange Rate Fluctuations on Overseas Investment of Asian Enterprises and Valuation of South Korean Listed Companies
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
Related Stocks
I will now provide you with a systematic and comprehensive analysis report.
Based on market data analysis, the South Korean won exchange rate has experienced significant fluctuations from 2025 to early 2026. It depreciated from around 1,400 KRW/USD at the beginning of the period to the current level of around 1,700 KRW/USD, with a depreciation rate of
- Exchange rate fluctuation range: 1,381 - 1,772 KRW/USD
- Average monthly volatility: approximately 20 KRW
- Maximum monthly fluctuation: approximately 32 KRW
- Current exchange rate level: approximately 1,700 KRW/USD[1]
The main driving factors for the depreciation of the won include:
- Strong US Dollar Cycle: Uncertainty in Federal Reserve interest rate policies has boosted the US Dollar Index
- Geopolitical Risks: The situation on the Korean Peninsula and Sino-US trade frictions have affected market sentiment
- Trade Structure Pressure: As an export-oriented economy, South Korea is highly sensitive to changes in global demand
- Changes in Foreign Capital Flows: In 2025, foreign investors net purchased KRW 147.1 trillion worth of South Korean bonds, representing a 96.4% increase compared to the previous year[2]
According to the latest reports, South Korea’s original large-scale investment plan in the United States is facing major adjustments:
| Indicator | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Investment Cap | $20 billion | Agreed in South Korea-US trade negotiations |
| Total Planned Investment | $350 billion | To be implemented over multiple years |
| Current Status | Unlikely to launch in the first half of the year | Statement from the South Korean Ministry of Economy and Finance |
| Completed Investment Scale | Approximately $41 billion | Mainly in the semiconductor sector[1][3] |
South Korea’s Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Economy and Finance Choo Kyung-ho clearly stated: “
The depreciation of the won has had a significant cost impact on the overseas investment of South Korean enterprises:
Cost Calculation Based on Exchange Rate Changes (Based on the $20 billion annual investment plan)
- Won depreciation rate: 21.4%
- Increase in investment costs: approximately $4.29 billion
- Impact on total plan ($350 billion): approximately $7.5 billion
For the long-term investment plan of $350 billion, this means a significant decline in the purchasing power of won-denominated assets, and enterprises need to bear higher financing costs and exchange losses.
The investment adjustments of South Korean enterprises have triggered a chain reaction across the entire Asian region:
- Major Asian economies such as Japan and Taiwan, China also face exchange rate fluctuation risks
- Enterprises generally adopt a “wait-and-see instead of aggressive expansion” strategy
- Investment decision-making cycles in the semiconductor industry have been extended[1]
According to survey data, South Korean financial companies have started to allocate dollar-denominated assets:
“When exchange rates are unstable, the risk of doing business and investing only in won is too high, and the trend of dollarization of assets will become more serious in the future.”[4]
- South Korean enterprises need to re-evaluate their production capacity layout in the United States and Southeast Asia
- “Cost sensitivity” has become a core consideration for investment location selection
- The trend of supply chain diversification has accelerated
Data shows that the won exchange rate has a
| Indicator | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| KOSPI Increase in 2025 | 76% | One of the best-performing markets globally |
| Correlation Between KOSPI and KRW | 0.936 | Strong positive correlation |
| KOSPI Level in Early 2026 | 4,885 points | Record high[2][5] |
The underlying logic of this phenomenon is as follows:
- Exchange Rate → Corporate ProfitPath: Won depreciation → Increase in foreign currency-denominated revenue of export enterprises → Profit growth → Stock price rise
- Liquidity Effect: Won-denominated assets have become more attractive to foreign investors
- Valuation Re-rating: Won-denominated South Korean assets have become relatively “cheaper”
Major South Korean enterprises show significant industry-specific differences in their sensitivity to exchange rate changes:
| Enterprise | Overseas Revenue Ratio | US Exposure | Net Impact of 10% Won Depreciation |
|---|---|---|---|
| SK Hynix | 90% | 40% | +15% |
| LG Energy Solution | 88% | 32% | +14% |
| Samsung Electronics | 85% | 35% | +12% |
| Samsung SDI | 75% | 28% | +11% |
| Kia Corporation | 65% | 30% | +10% |
| Hyundai Motor Company | 70% | 25% | +8% |
| Hyosung Corporation | 60% | 22% | +7% |
| POSCO Holdings | 55% | 20% | -5% |
- Export-oriented enterprises(semiconductors, automobiles) have generally benefited from won depreciation
- Raw material import-oriented enterprises(steel) may be negatively impacted
- Average Net Impact: A 10% depreciation of the won brings an average net profit increase of about 9%[1]
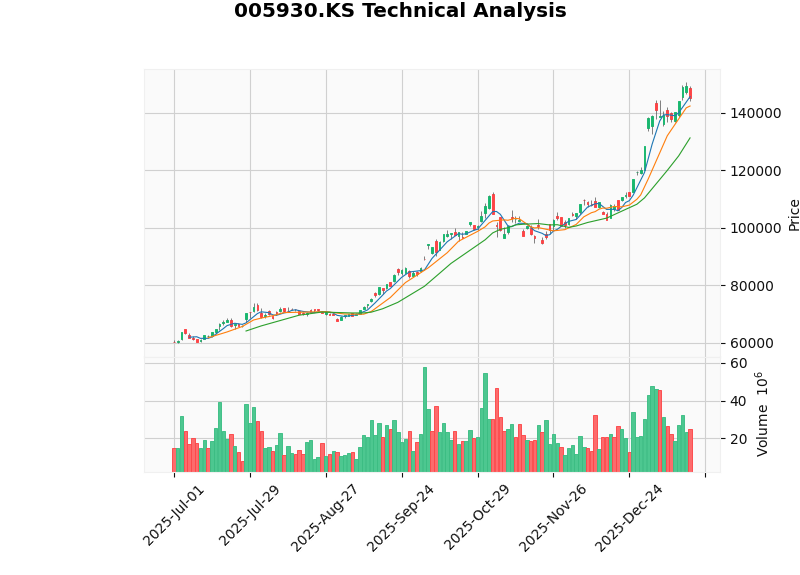
As South Korea’s largest listed company by market capitalization, the valuation of Samsung Electronics (005930.KS) is representative:
- Current Price: KRW 145,200
- Trading Range: KRW 131,205 - 147,539
- Trend Judgment: Sideways Trading(no clear trend)
- Beta Coefficient: 0.83 (relatively stable compared to US stocks)[6]
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: 29.86x
- Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio: 2.52x
- EV/Operating Cash Flow (EV/OCF): 11.94x
- Accounting Policy: Conservative(high depreciation/capital expenditure ratio)
- Debt Risk: Low
- Return on Equity (ROE): 8.39%
- Net Profit Margin: 10.38%[6][7]
Multi-dimensional impacts of won exchange rate fluctuations on the valuation of South Korean listed companies:
| Impact Dimension | Transmission Mechanism | Valuation Impact Direction |
|---|---|---|
Profit Side |
Conversion of export revenue | Positive (increase in foreign currency-denominated revenue) |
Cost Side |
Rise in imported raw material prices | Negative (increase in won-denominated costs) |
Cash Flow |
Fluctuations in operating cash flow | Neutral to positive |
Valuation Multiples |
Adjustment of risk premium | May come under pressure |
Foreign Capital Inflows |
Exchange rate arbitrage transactions | Positive driving force |
-
Persistent Exchange Rate Fluctuation Risk
- Won volatility is at a historical high
- Divergence in monetary policies increases uncertainty
-
Geopolitical Risks
- Persistent US semiconductor tariff threats (up to 100% tariffs)[1]
- The situation on the Korean Peninsula affects risk premiums
-
Valuation Correction Risk
- The KOSPI faces technical adjustment pressure after a 76% increase in 2025
- Societe Generale pointed out: The bull market is mainly supported by domestic institutions, with “retail investors absent”[2]
-
Transmission of External Shocks
- The Bank of Korea warns: If US stocks fall by 30%, South Korean exports may decline by 1.7 percentage points[2]
-
Enhanced Export Competitiveness
- Won depreciation enhances the price competitiveness of South Korean products
- Export advantages in semiconductors, displays, automobiles, etc. are consolidated
-
Foreign Capital Allocation Demand
- Net inflows of KRW 147.1 trillion into South Korean bonds in 2025[2]
- Expected inclusion in the WGBI (World Government Bond Index) attracts passive capital
-
Opportunity for Industrial Upgrading
- Exchange rate pressure accelerates the improvement of enterprise efficiency
- The proportion of high-value-added products increases
-
Won exchange rate fluctuations have substantially affected cross-border investment decisions: The $20 billion annual investment plan is facing suspension, reflecting the significant constraint of exchange rate risks on capital allocation.
-
South Korean listed companies have generally benefited from local currency depreciation: Export-oriented enterprises (semiconductors, automobiles) have seen significant improvements in profitability, with an average net impact of approximately +9% (in the scenario of a 10% won depreciation).
-
Valuation has a strong positive correlation with exchange rate: The correlation between KOSPI and KRW reaches 0.936, with exchange rate fluctuations transmitted through multiple channels including profitability, liquidity, and valuation.
-
Structural differentiation has intensified: Attention should be paid to the valuation pressure on enterprises with high foreign debt and raw material import-oriented enterprises.
| Strategy | Specific Recommendations |
|---|---|
Bullish |
Leading enterprises in exchange rate-sensitive industries such as semiconductors and export automobiles |
Avoid |
Enterprises with high US dollar debt, raw material importers |
Hedge |
Pay attention to tools such as won options and currency swaps |
Allocation |
Appropriately increase allocation of won-denominated assets to benefit from both exchange rate appreciation and valuation growth |
[1] Wall Street CN - “Regarding the $350 billion South Korea-US Investment, South Korea Worries About ‘Large-Scale Capital Outflows’” (https://wallstreetcn.com/articles/3763550)
[2] Caixun Express - “South Korean Stocks Surge 76% in 2025! Societe Generale Says It’s Mainly Supported by Domestic Institutional Investors, with Retail Investors Absent from the Bull Market” (https://tw.stock.yahoo.com/news/)
[3] People’s Daily Online - “Regarding US New Tariff Threats to the Semiconductor Industry, South Korea Cautiously Evaluates Large-Scale Investment in the US” (http://korea.people.com.cn/n1/2026/0119/c407882-40648076.html)
[4] Maeil Business Newspaper - “The CEO of a domestic financial company…” (https://www.mk.co.kr/cn/economy/11938172)
[5] Gilin API Market Data - KOSPI Index and KRW Exchange Rate Data [0]
[6] Gilin API Technical Analysis - Samsung Electronics Technical Indicators [0]
[7] Gilin API Financial Analysis - Samsung Electronics Financial Statement Analysis [0]
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.