IBM Unveils Advanced Quantum Computers Nighthawk and Loon: Technical Breakthrough and Market Impact Analysis
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
Related Stocks
This analysis is based on IBM’s announcement of two advanced quantum computing chips at the Quantum Developer Conference 2025 in Atlanta on November 12, 2025 [1][2][3]. The launch represents a significant milestone in IBM’s quantum computing roadmap and positions the company competitively in the rapidly evolving quantum computing landscape.
The launch includes significant software advances, including a 24% increase in circuit accuracy at 100+ qubits, 100x reduction in cost of obtaining accurate results, and 10x acceleration in quantum error correction decoding delivered one year ahead of schedule [2].
The global quantum computing market is experiencing explosive growth, with 2025 market size estimates ranging from $1.44 billion to $3.52 billion, projected to reach $16.22-$31.26 billion by 2031-2034, representing a CAGR of 30.88%-41.8% through 2030 [5][6]. North America currently dominates with over 40% market share [5].
IBM faces competition from major technology players including Google (Willow chip with “Quantum Echoes” algorithm), Microsoft (topological qubits approach), Amazon Web Services (quantum cloud services), and specialized quantum companies like IonQ, Quantinuum, D-Wave, and Rigetti Computing [2][3][5].
IBM leverages its semiconductor manufacturing capabilities at the Albany NanoTech Complex, which houses the same advanced chipmaking tools as leading semiconductor fabs [1]. The company has achieved a 10X increase in chip complexity while halving development time, with advanced 300mm wafer production enabling improved qubit density and performance [2].
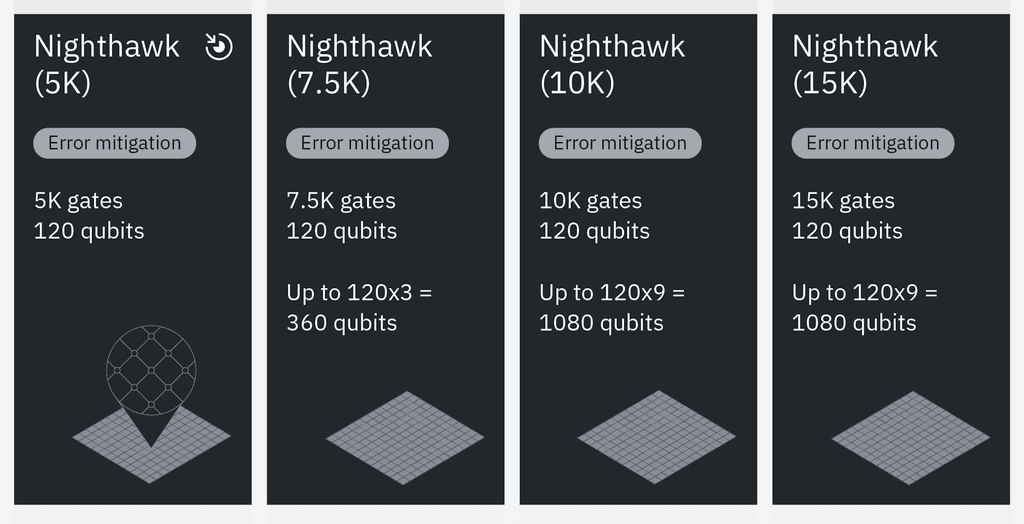
IBM’s approach emphasizes qubit connectivity and error correction rather than pure qubit count, differentiating from competitors focused primarily on increasing qubit numbers [2]. The 218 couplers in Nighthawk enable enhanced connectivity and error correction capabilities, potentially providing a more practical path to quantum advantage [3][4].
The launch demonstrates IBM’s commitment to hybrid classical-quantum computing, with real-time error decoding and integration with classical HPC environments through enhanced Qiskit SDK featuring new C++ interface [2]. This approach aligns with industry trends recognizing that practical quantum computing will require tight integration with classical systems.
IBM’s open-source Qiskit platform creates developer lock-in and ecosystem effects, while the community-led verification system establishes industry standards for quantum advantage claims [3]. This ecosystem approach could provide sustainable competitive advantages as the quantum computing market matures.
The increased connectivity requirements make quantum chips significantly harder to build due to the need for both qubits and complex quantum connections [1]. Yield and consistency challenges in producing high-quality quantum processors at scale remain significant concerns. Performance validation requires rigorous verification and community validation, with timeline uncertainty in achieving fault-tolerant quantum computing by 2029 [1].
Major competitors with substantial resources are accelerating their quantum programs, potentially compressing IBM’s timeline advantage [2][5]. Alternative quantum approaches including trapped ions, neutral atoms, and topological qubits may prove more viable than superconducting qubits [5]. Enterprise adoption patterns will depend on demonstrating clear ROI versus classical computing solutions.
IBM’s manufacturing advantage through the Albany NanoTech Complex provides scale capabilities that may become increasingly important as quantum computing matures [1][2]. The clear roadmap with specific milestones toward quantum advantage by 2026 and fault-tolerant systems by 2029 offers measurable progress tracking. The integrated approach combining hardware, software, and error correction could provide comprehensive solutions difficult for competitors to replicate.
IBM’s quantum computing launch represents a strategic advancement in the company’s long-term technology roadmap. The Nighthawk and Loon chips demonstrate significant technical progress in qubit connectivity and error correction, with clear development milestones through 2028 [2][3][4]. The company leverages its semiconductor manufacturing capabilities at the Albany NanoTech Complex to achieve scale advantages [1][2].
The quantum computing market’s projected growth to $16-31 billion by 2031-2034 provides significant opportunity, though competitive pressures from major technology companies and alternative quantum approaches create uncertainty [5][6]. IBM’s focus on ecosystem development through Qiskit and community verification systems may provide sustainable advantages [2][3].
Technical challenges in manufacturing complexity and yield remain significant risks, as does timeline uncertainty in achieving practical quantum advantage [1]. The company’s integrated hardware-software approach and clear roadmap position it competitively, though execution risk and market adoption patterns will be critical factors in determining long-term success.
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.