Analysis of the Impact of Intel's Yield Issues on AI Chip Market Competition and Capacity Supply
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
Related Stocks
Now I will prepare a systematic and comprehensive analysis report integrating all collected data:
Based on the latest financial data, Intel openly disclosed severe challenges in its manufacturing segment during its Q4 2025 earnings call. CEO Chen Liwu clearly stated: “Our current yield and production levels have not met standards, and we must improve as soon as possible.”[1][2]
- 18A Process Yield: According to KeyBanc Capital Markets analysis, the 18A yield was approximately 55% in mid-2025, currently increasing by 7%-8% per month, but still not reaching industry-leading levels[3]
- Capacity Utilization: Factories are operating at full capacity, but the proportion of usable chip output is insufficient, directly limiting delivery capabilities[2]
- Inventory Level: Inventory in Q4 has dropped to 40% of its peak, further highlighting capacity pressure[4]
| Financial Indicator | Q4 2025 Data | Year-over-Year Change | Market Expectation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | $13.67 billion | -4.1% | $13.43 billion |
| Adjusted EPS | $0.15 | +15.4% | $0.09 |
| Gross Margin | 37.9% | - | ~40% |
| Expected Q1 EPS | $0 (Break-even) | - | $0.08 |
The yield issue has directly pressured gross margin; the company expects gross margin to further decline to 34.5% in Q1 2026, a far cry from its peak level of over 60%[2]
Intel’s AI chip market share is experiencing a catastrophic decline. From 2021 to 2025, the market landscape has undergone a fundamental shift:
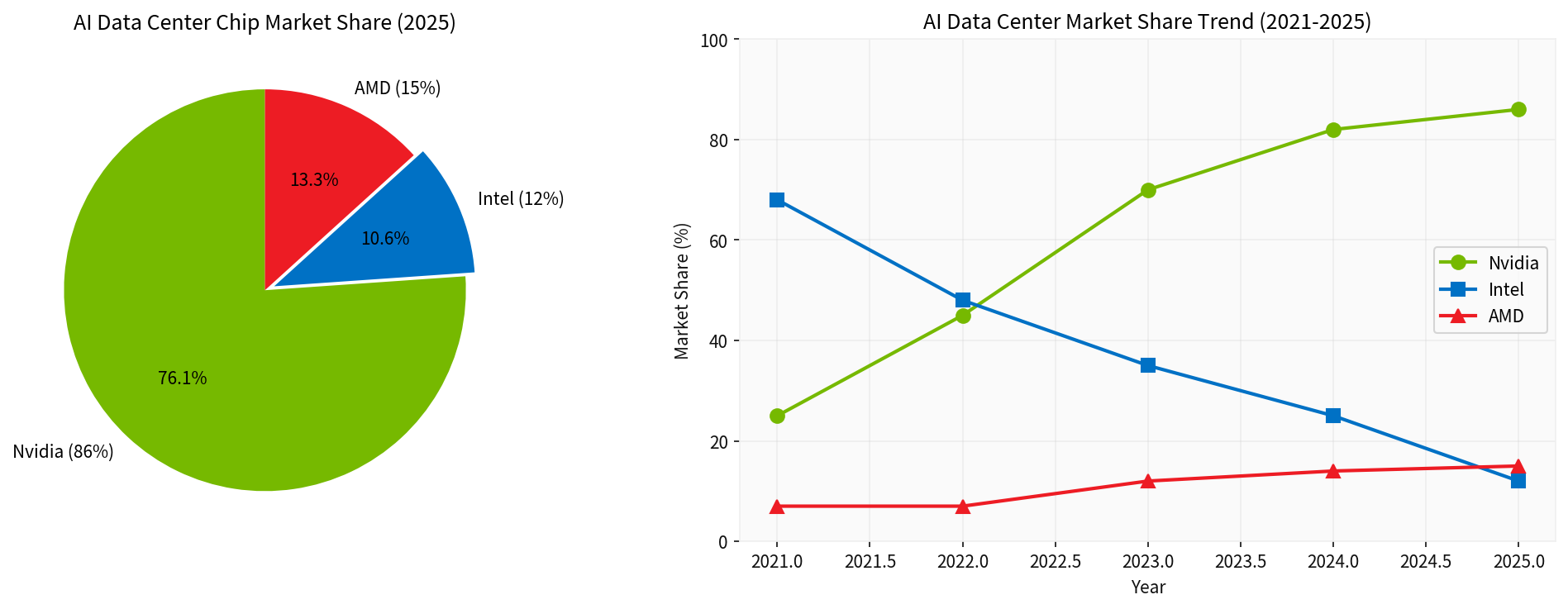
| Year | NVIDIA | Intel | AMD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 25% | 68% |
7% |
| 2022 | 45% | 48% | 7% |
| 2023 | 70% | 25% | 12% |
| 2024 | 82% | 15% | 14% |
| 2025 | 86% |
12% |
15% |
This data reveals that Intel’s dominant position in the AI data center market has been completely replaced by NVIDIA. The launch of ChatGPT at the end of 2022 became a critical turning point, as large tech companies accelerated the construction of AI data centers, leading to a surge in demand for GPU-intensive infrastructure, which Intel failed to capitalize on in a timely manner[5]
- In 2026, full-scale mass production of the Vera Rubin platform for AI data centers has been launched
- GPU TDP increased to 2.3kW, memory bandwidth reaching 22.2 TB/s
- Full-chain platform advantages from chips to entire AI systems
- AI computing performance nearly doubles annually[5]
- Achieved leaps in performance, energy efficiency, and multi-core capabilities
- Announced deep collaboration with OpenAI in October 2025
- Client market share: Intel holds approximately 60%, AMD’s desktop segment exceeds 30%[6]
Intel admitted during the earnings call that it failed to fully capture market demand due to capacity constraints[4]:
- Tight Supply of Data Center CPUs: Despite surging demand for Xeon processors from AI servers, factory capacity cannot meet the need
- Capacity Reallocation: Intel has reallocated wafer fab capacity from client chips to Xeon processors to prioritize meeting cloud computing and enterprise-level AI training/inference needs[7]
- Limited Delivery Capabilities: The company cannot keep up with chip demand, leaving behind profitable data center sales opportunities[8]
| Time Node | Capacity Expectation |
|---|---|
| Q1 2026 | Usable supply drops to the lowest level |
| Q2 2026 | Gradual improvement begins |
| H2 2026 | Accelerated improvement in yield and capacity utilization |
- April 2025: Entered risk production
- October 2025: Full-scale production launched
- End of 2025: Arizona factory enters mass production ramp-up
- January 5, 2026: Fab 52 facility officially reached High-Volume Manufacturing (HVM) status[3]
- RibbonFET Technology: The transistor current channel is made into a nanoscale “ribbon”, with the gate wrapping around from four sides to control current switching
- PowerVia Backside Power Delivery Technology: Moves power supply circuits to the back of the transistor layer, providing more routing space and reducing voltage loss
- Performance Improvement: Over 15% performance improvement at the same power consumption, over 25% power reduction at the same performance, and 30% higher transistor density[1]
Facing tight capacity of TSMC’s CoWoS packaging, Intel’s EMIB technology has become a key differentiator:
| Feature | Intel EMIB | TSMC CoWoS |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Simplified, no expensive interposer required | Requires large-area interposer |
| Yield | Relatively higher | Limited by complex structure |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | Minimal issues | Significant matching challenges |
| Package Size | EMIB-M supports 6x reticle, expected to reach 8-12x in 2026-2027 | CoWoS-L currently 3.5x, expected to reach 9x in 2027 |
| Cost | More cost-effective | Relatively high price |
- Apple, Qualcomm, Google, Meta are evaluating EMIB for AI accelerators/data center chips
- Microsoft Maia, AWS Trainium have entered the testing phase[1]
In 2025, under the leadership of CEO Chen Liwu, Intel received over $15 billion in investments[1]:
| Investor | Amount | Time | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. Government | $8.9 billion | August 2025 | Acquired 9.9% stake to become a major shareholder |
| SoftBank Group | $2 billion | August 2025 | Subscribed at $23 per share |
| NVIDIA | $5 billion | September 2025 | Invested at $23.28 per share |
- Microsoft expanded its partnership with Intel to manufacture custom “Maia 2” AI accelerators
- NVIDIA has also begun using Intel’s advanced packaging services, reflecting a “co-opetition” relationship[3]
CEO Chen Liwu clearly stated three priorities during the earnings call[1][2]:
- Improve Execution: The core challenge lies in the need for significant improvement at the execution level
- Revitalize Engineering Excellence: Continue to advance 18A and 14A processes
- Seize AI Opportunities: Firmly believe in the core role of CPUs in the AI era
| Product | Status | Target Market |
|---|---|---|
| Panther Lake (18A Consumer) | Mass production ramp-up, launched at CES 2026 | AI PC market |
| Clearwater Forest (18A Server) | Mass production | Cloud and enterprise-level AI training/inference |
| Nova Lake | Launch by end of 2026 | Client market |
| 14A Process | 2028 | External foundry customers |
- HSBC raised its target price from $26 to $50
- Citigroup upgraded its rating from “Sell” to “Neutral” with a target price of $50
- KeyBanc upgraded to “Overweight”
- Intel’s stock price rose 47% in 2026, ranking third in the S&P 500 gain list[1]
- Bernstein analyst Stacy Rasgon: Market share loss in the server business
- Customers still prefer older products, demand for new products is unclear
- Inventory risk in the PC business, which may be exacerbated if memory prices rise[1]
-
Short-Term Difficulty in Breaking Yield Bottleneck: Although the 18A yield continues to improve (7%-8% per month), it still lags behind industry-leading levels, and supply will remain tight in Q1 2026
-
Irreversible Market Share Loss: Plummeting from 68% to 12%, Intel has been completely overtaken by NVIDIA in the AI chip segment, making it difficult to recapture lost ground in the short term
-
Differentiated Competitive Strategy Emerges: EMIB advanced packaging and external foundry business have become breakthrough points, and competitors such as Microsoft and NVIDIA have also begun using its packaging services
-
Enhanced Capital and Strategic Support: Investments from the U.S. government, SoftBank, and NVIDIA provide financial buffers and strategic synergy
- Short-Term (H1 2026): Supply tightness will persist, with Q1 being the most constrained period, and gradual improvement starting in Q2
- Mid-Term (H2 2026): 18A capacity ramp-up will accelerate, and supply capacity will improve significantly after yield targets are met
- Long-Term (2027+): The 14A process will be launched, external foundry customer decisions will be finalized, and the foundry business is expected to become a new growth driver
Intel has shifted from a leader to a follower in the AI chip market, but its advantages such as leading 18A process technology, differentiated advanced packaging, and U.S. government support still leave a chance for a comeback. 2026 will be a crucial year for Intel to fulfill its commitment to “improved execution”; the progress of yield improvement and the expansion of foundry business will determine its final position in AI chip competition.
[1] 36Kr - “Intel Announces Q4 2025 Earnings, Revenue Reaches $13.67 Billion” (https://m.36kr.com/p/3651185379090567)
[2] NetEase News - “Intel’s Q4 2025 Revenue Reaches $13.7 Billion, Missing Expectations, Down 4.1% Year-over-Year” (https://www.163.com/dy/article/KJUL2O0V0511B8LM.html)
[3] Forbes - “Intel Foundry In 2026: An Inflection Point?” (https://www.forbes.com/sites/greatspeculations/2026/01/09/intel-foundry-in-2026-an-inflection-point/)
[4] Wall Street CN - “AI Demand Booms But Intel’s Capacity Is Strained? CEO Admits During Earnings Call” (https://www.cls.cn/detail/2267399)
[5] Sohu - “4 Years of Major Shuffling! Evolution of AI Data Center Revenue Among the Three Chip Giants” (https://m.sohu.com/a/978889787_121228203)
[6] Moomoo - “CPU Replica Storage Narrative! Intel’s Earnings Are Coming, AMD Aims for New Highs” (https://www.moomoo.com/hant/community/feed/cpu-replica-storage-story-intel-s-earnings-reports-is-coming-115938219196421)
[7] The Register - “Intel puts consumer chip production on back burner as datacenters make a run on Xeons” (https://go.theregister.com/feed/www.theregister.com/2026/01/23/intel_earnings_q4_2025/)
[8] Slashdot - “Intel Struggles To Meet AI Data Center Demand” (https://slashdot.org/story/26/01/22/2317238/intel-struggles-to-meet-ai-data-center-demand/)
零跑汽车子公司325%增资战略分析
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.