Main Force Capital Accumulation in the Power Equipment Sector: In-Depth Analysis of Industry Logic and Investment Sustainability
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
Related Stocks
Based on the above in-depth analysis, I present to you a complete analysis report on the continuous capital accumulation by main forces in the power equipment sector:
The power equipment sector has recently seen continuous capital accumulation by main forces, mainly driven by
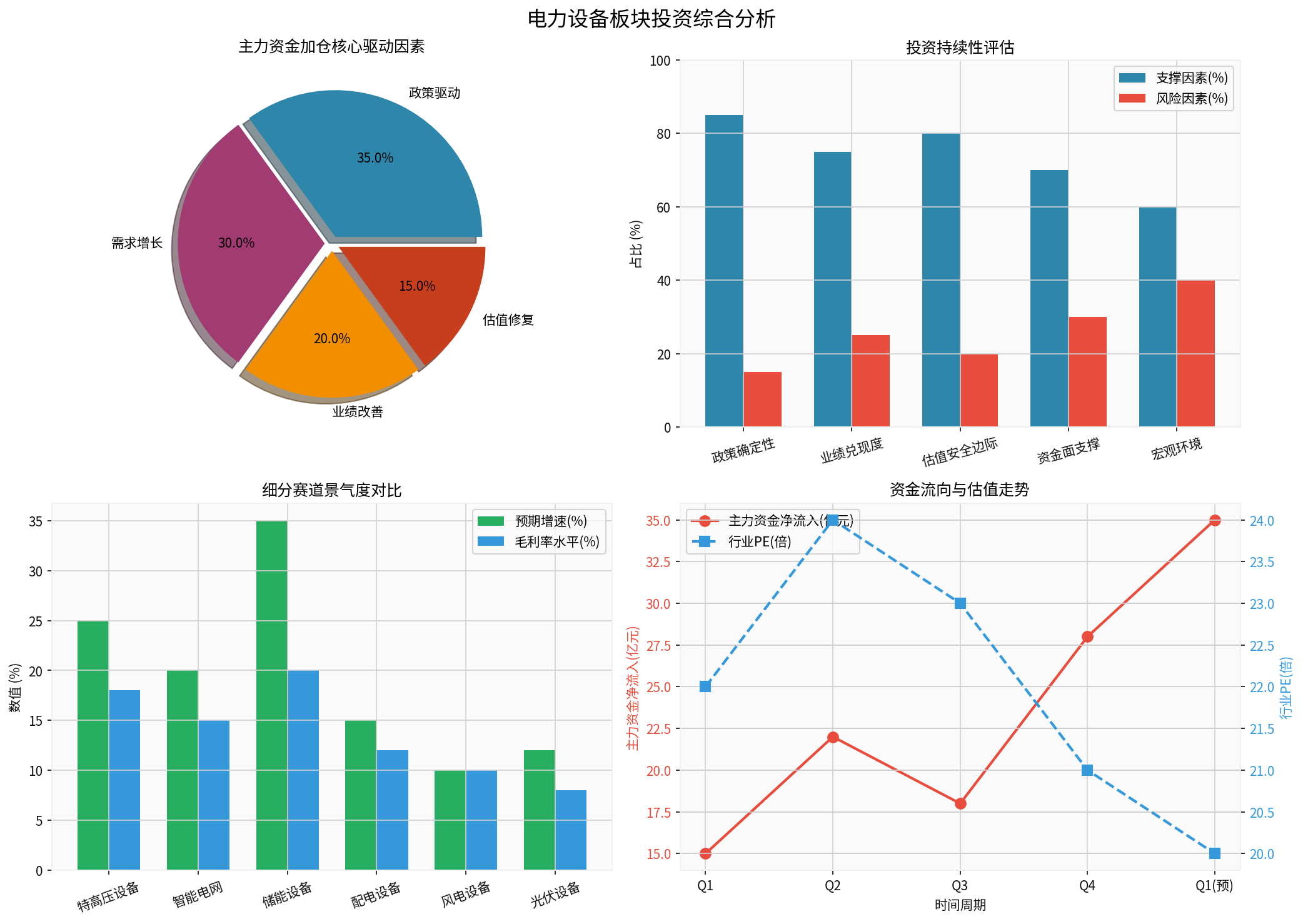
The chart above shows the analysis of investment drivers, sustainability assessment, prosperity comparison of sub-sectors, as well as capital flow and valuation trends of the power equipment sector.
According to recent market data, the power equipment sector, together with the computer, non-ferrous metals, national defense and military industry, and mechanical equipment sectors, constitutes the main direction of main force capital inflows, while sectors such as communications, electronics, banking, household appliances, and food and beverage show net outflows.
| Capital Flow Characteristics | Market Implications |
|---|---|
| Capital shifts from high-valuation to low-valuation sectors | Market risk appetite declines, with a focus on certain returns |
| Rotation from TMT to manufacturing | Crowded technology sectors are sold off, while manufacturing gains favor |
| Counter-cyclical attributes are recognized | Power grid investment is valued as an important tool for stable growth |
At the individual stock level, targets such as
- Continuous advancement of the “Dual Carbon” goals: The construction of new power systems has been elevated to a national strategy, accelerating energy structure transformation
- Prominent counter-cyclical adjustment role: Power grid investment has become an important tool for stable growth, with high growth certainty in the 2025 investment plan
- Supported by energy security strategy: There is an urgent demand for power infrastructure upgrading, accelerating the construction of UHV projects
| Policy Type | Specific Content | Impact on the Sector |
|---|---|---|
| New power system planning | Building a clean, low-carbon, safe and efficient energy system | High certainty of long-term demand |
| UHV construction | Launch of a new round of transmission channel construction | Directly drives equipment demand |
| Distribution network transformation | Intelligent and digital upgrading | Smart meters and distribution automation benefit |
- New energy grid connection demand: Wind power and photovoltaic installed capacity continue to grow, driving demand for power grid transformation
- UHV construction peak: Accelerated construction of cross-regional transmission channels, driven by new energy consumption pressure
- Intelligent transformation of distribution networks: Demand for distributed energy access is released, with huge space for intelligent transformation
- Energy storage supporting demand: Driven by new energy supporting energy storage policies, demand for energy storage equipment grows rapidly
| Sub-Sector | Expected Annual Growth Rate | Core Driving Factors |
|---|---|---|
| UHV equipment | 25%+ | Cross-regional transmission of new energy |
| Smart meters | 15-20% | Launch of replacement cycle |
| Distribution automation | 15-20% | Urbanization construction |
| Energy storage equipment | 30%+ | Driven by supporting energy storage policies |
- Revenue side improvement: The growth rate of power grid investment rebounded significantly in 2024, accelerating the pace of order delivery
- Cost side stabilization: Prices of raw materials (copper, aluminum, steel) have retreated from highs, leaving room for gross profit margin recovery
- Expense ratio optimization: Scale effects are released, with management expense ratio and sales expense ratio expected to decline further
- Historically low range: The PE of the power equipment sector is at a historical low, with limited downside risk
- Significant valuation discount: There is a significant discount compared to the new energy sector, with sufficient safety margin
- Room for institutional position increase: Compared to popular sectors such as TMT, the proportion of institutional holdings still has room for growth
- High dividend attractiveness: Leading companies have favorable dividend yields, attracting long-term capital
| Supporting Factors | Support Degree | Core Logic |
|---|---|---|
| High policy certainty | 85% | The new power system construction plan is long-term, and power grid investment is a key focus of the “14th Five-Year Plan” |
| Good performance fulfillment | 75% | Power grid order execution cycles are long, with high performance certainty; leading enterprises have sufficient order reserves |
| Sufficient valuation safety margin | 80% | The sector’s PE is at a historical low, and leading companies have favorable dividend yield protection |
| Capital side still has support | 70% | Institutional holdings are relatively low, and long-term funds such as social security and insurance prefer such targets |
| Risk Factors | Risk Degree | Response Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Macroeconomic fluctuation risk | 40% | Monitor macroeconomic data; power grid investment has certain counter-cyclical attributes |
| Raw material price fluctuation risk | 30% | Track commodity trends; select targets with stable gross profit margins |
| Risk of intensified industry competition | 25% | Focus on leading enterprises; avoid low-end product competition |
| Accounts receivable recovery risk | 20% | Monitor cash flow status; prioritize targets with strong collection capabilities |
- Construction Logic: Accelerated construction of cross-regional transmission channels, with strong demand for new energy consumption
- Competitive Landscape: Core equipment such as converters and transformers have high barriers, with high concentration of leading enterprises
- Growth Expectation: Annual growth rate is expected to remain above 25%
- Gross Profit Margin Level: 18-22%, with strong profitability
- Construction Logic: Demand for intelligent transformation of distribution networks is released, driven by distributed energy access
- Competitive Landscape: There are many sub-sectors, with relatively scattered competition
- Growth Expectation: Annual growth rate is expected to remain 15-20%
- Gross Profit Margin Level: 15-18%, relatively stable
- Construction Logic: Driven by new energy supporting energy storage policies, energy storage installed capacity grows rapidly
- Competitive Landscape: The industry is in a rapid development stage, with an unstable competitive landscape
- Growth Expectation: Annual growth rate is expected to remain above 30%
- Gross Profit Margin Level: 20-25%, with room for improvement
- Construction Logic: Urbanization drives growth in distribution network investment
- Competitive Landscape: Competition is relatively fierce, with room for concentration improvement
- Growth Expectation: Annual growth rate remains 10-15%
- Gross Profit Margin Level: 12-15%, relatively stable
The power equipment sector has
| Time Horizon | Investment Logic |
|---|---|
| Short-term (1-3 months) | Valuation recovery driven by market style rotation |
| Medium-term (3-6 months) | Performance improvement driven by order fulfillment |
| Long-term (6-12 months) | Continuous advancement of new power system construction |
| Allocation Ratio | Allocation Direction | Specific Target Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Core allocation (60%) | Leading UHV equipment, leading energy storage equipment | With core technological barriers and full order books |
| Satellite allocation (30%) | High-quality targets in smart power grids and distribution equipment | Sub-sector leaders with reasonable valuations |
| Cash position (10%) | To cope with market volatility | Maintain flexibility and seize accumulation opportunities |
- Leading Enterprises: Scale effects from market share expansion
- Gross Profit Margin Improvement: Stabilized raw material prices + product structure upgrading
- Order Structure: High proportion of orders from high-prosperity sectors such as UHV/energy storage
- Overseas Expansion: Power grid construction demand in countries along the Belt and Road
- Risk of power grid investment falling short of expectations: If the macroeconomy declines significantly, it may affect the pace of power grid investment
- Risk of sharp fluctuations in raw material prices: Raw materials such as copper and aluminum account for a high proportion of costs, and price fluctuations affect gross profit margins
- Risk of intensified industry competition: Price wars may erode profit margins
- Risk of weakened policy support: Monitor the impact of policy changes on sector valuation
The continuous capital accumulation by main forces in the power equipment sector is supported by
[0] Jinling AI Financial Data Analysis System - Market Capital Flow and Industry Analysis Data
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.