Swiss Inflation Declines to 0.1% in October 2025 Amid SNB Policy Considerations
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
This analysis is based on the Wall Street Journal report [1] published on November 3, 2025, which reported Swiss inflation declining to 0.1% in October as the Swiss National Bank considers negative interest rates.
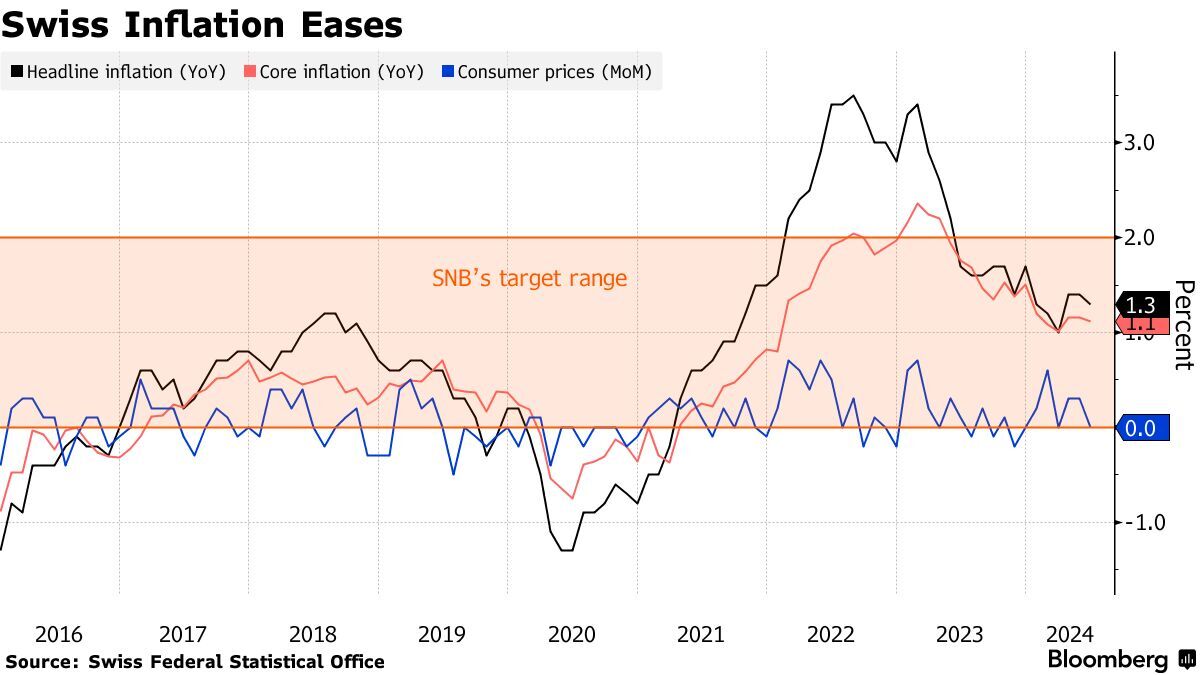
Swiss annual inflation fell to 0.1% in October 2025, down from 0.2% in September, representing the lowest inflation rate since June 2025 [1][2]. This reading came at the lower end of market expectations, which ranged from +0.1% to +0.4% according to AWP surveys [2]. The monthly Consumer Price Index (CPI) declined by 0.3% to 107.2 points, driven primarily by lower prices in the hotel industry, package tours abroad, and private transportation rentals [2].
The inflation data reveals significant divergence between domestic and imported goods:
- Domestic goods inflation:+0.5% YoY in October
- Imported goods inflation:-1.3% YoY (down from -0.9% in September)
- Core inflation:+0.5% (down from +0.7% in September) [2]
This disparity indicates that Swiss franc strength is significantly impacting import prices while domestic price pressures remain more stable.
The Swiss National Bank (SNB) currently maintains its policy rate at 0%, with a 0.25 percentage point discount on sight deposits above the set threshold [3]. The persistent low inflation environment significantly impacts Swiss monetary policy considerations, with the SNB potentially considering negative rates to counteract currency appreciation [1][4].
Swiss inflation has been on a declining trend since the 2022-2023 peak when it exceeded 3% [3]. The October 2025 reading represents a dramatic normalization from those elevated levels, though it also raises concerns about insufficient price growth. The SNB’s inflation projections for 2025-2027 remain modest at 0.2%, 0.5%, and 0.7% respectively, assuming the policy rate stays at 0% [3].
The Swiss franc’s safe-haven status has led to sharp appreciation against major currencies, reaching levels seen only during the Eurozone sovereign debt crisis and the January 2015 euro peg abandonment [4]. The currency has gained more than 10% against the USD and over 6% in trade-weighted terms [4]. This appreciation, combined with external pressures including U.S. tariffs weighing on the Swiss economic outlook, creates additional economic challenges [4].
The combination of sub-1% inflation and continued franc appreciation creates genuine deflationary pressures that could impact consumption and investment decisions. The SNB faces a complex policy dilemma: maintaining current rates risks allowing deflationary pressures to strengthen, while shifting to negative rates could squeeze bank profitability and potentially lead to rapid credit growth [4].
The significant divergence between domestic goods inflation (+0.5%) and imported goods inflation (-1.3%) highlights the asymmetric impact of currency strength across the economy. The hotel and tourism sectors experienced notable price declines, reflecting both currency effects and seasonal factors [2]. This suggests that export-oriented and tourism-dependent sectors may face disproportionate challenges compared to domestically-focused businesses.
The fact that October inflation came in at the lower end of market expectations suggests that deflationary pressures may be stronger than anticipated [2]. Current market sentiment appears cautiously optimistic about Switzerland’s ability to maintain price stability, though concerns about growth persist. The inflation trajectory from the 2022-2023 peak above 3% to the current 0.1% represents one of the most rapid disinflationary episodes among developed economies [3].
- Deflation Risk:The combination of very low inflation and currency appreciation could rapidly exacerbate deflationary risks and result in weaker economic growth [4].
- Policy Response Risk:The SNB’s potential shift to negative rates could have unintended consequences for the banking sector and financial stability [4].
- External Shock Vulnerability:Switzerland’s export-oriented economy remains vulnerable to global trade tensions and currency volatility, with potential additional U.S. tariffs on pharmaceuticals posing downside risks [4].
- Growth-Inflation Trade-off:Policy measures to support inflation may conflict with broader economic growth objectives.
Decision-makers should closely monitor:
- SNB policy statements and intervention activities in forex markets
- Swiss franc exchange rate movements, particularly EUR/CHF levels
- Quarterly GDP growth data and business confidence indicators
- Inflation expectations from surveys and market-based measures
- Banking sector profitability and credit growth metrics
Swiss inflation at 0.1% in October 2025 reflects the ongoing challenge of balancing price stability with economic growth in an environment of currency appreciation and external pressures. The SNB’s policy rate at 0% may need adjustment if deflationary risks intensify, though negative rates present their own set of challenges for the financial system. The significant divergence between domestic and imported goods inflation underscores the uneven impact of currency strength across economic sectors. Market participants should remain attentive to SNB guidance, currency developments, and external trade factors that could influence Switzerland’s economic trajectory.
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.